Page 141 - Nighthawk_Partsbook_2021_1.2.0
P. 141
Bearing
Information
Description
Ball bearings are used to provide smooth, low friction motion in rotary applications. Ball bearings are
able to provide high performance and long lifetime in order to transfer the load from the balls to the
inner races. The balls have minimal contact with the inner and outer races due to their spherical shape
and this allows them to spin smoothly.
A disadvantage of ball bearings is that the balls can become "flattened" over time with too much
pressure on the outer races leading to eventual failure. Therefore it is very important that the load
ratings and other parameters are monitored regularly.
Parts
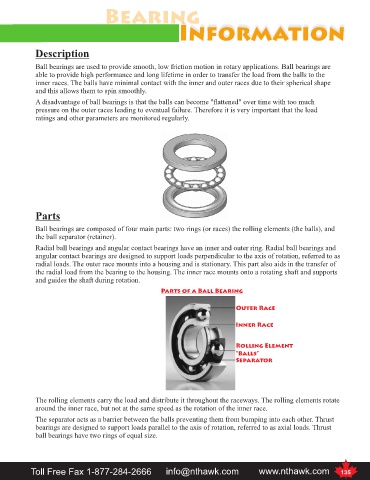
Ball bearings are composed of four main parts: two rings (or races) the rolling elements (the balls), and
the ball separator (retainer).
Radial ball bearings and angular contact bearings have an inner and outer ring. Radial ball bearings and
angular contact bearings are designed to support loads perpendicular to the axis of rotation, referred to as
radial loads. The outer race mounts into a housing and is stationary. This part also aids in the transfer of
the radial load from the bearing to the housing. The inner race mounts onto a rotating shaft and supports
and guides the shaft during rotation.
Parts of a Ball Bearing
Outer Race
Inner Race
Rolling Element
“Balls”
Separator
The rolling elements carry the load and distribute it throughout the raceways. The rolling elements rotate
around the inner race, but not at the same speed as the rotation of the inner race.
The separator acts as a barrier between the balls preventing them from bumping into each other. Thrust
bearings are designed to support loads parallel to the axis of rotation, referred to as axial loads. Thrust
ball bearings have two rings of equal size.
Toll Free Fax 1-877-284-2666 info@nthawk.com www.nthawk.com 135